Installation of the coulometer LCD display
The previous post in the powerbox project:
https://bkhome.org/news/202004/wiring-board-installed-in-powerbox.html
The finishing touch is to install and calibrate the Amptron
coulometer. As already discussed, the shunt is already mounted on the
wiring-board. This is what I have:
https://www.amptron.com.au/100a-coulometer---battery-monitor-with-shunt.html
If you search on eBay and elsewhere, for "battery coulometer", you
will find this available from many vendors, and there are also setup
videos on YouTube.
Installing the coulometer
There is a shielded cable to connect the shunt to the LCD display,
and this is a problem, as it is very long. This is for the situation
where you want the display somewhere else, maybe on the dashboard of the
vehicle, or whatever.
I want to cut it right down, as the LCD display is close to the
shunt. So, I cut the plugs off each end, and joined the cable. I am
familiar with delicate electrical work, as I was an electronic engineer
in my working days. I have a small soldering iron and fine solder for
the purpose. The wires inside this cable are so tiny, this photo blows
it up, but in actuality they are so tiny. The photo shows after I have
stripped each wire and twisted them together:

...I then very carefully soldered each join, then put heatshrink
tubing over each join, then bound it all together with electrical tape.
I know that such delicate work will be a challenge for many -- well,
you could just go and buy a ready-made powerbox! But it is not
insurmountable. The wires are so tiny, I stripped them with my
thumbnail, pressing onto the table -- my cable stripper does not handle
such tiny wire.
Calibrating the coulometer
I watched one of the YouTube videos on how to calibrate the
coulometer, but it is misleading. They set "full" and "empty"
corresponding to certain battery voltages, but this could be very
inaccurate.
Here are the instructions:


What I did was first charge the battery to 100%, using the Amptron mains-input lithium 15A battery charger:
https://www.amptron.com.au/15a-12v-lithium-lifepo4-battery-charger.html
...this has eyelet lugs, that I replaced with a black Anderson plug
-- very convenient, just plug it into the powerbox, and it will charge
until 100%.
Following the above instructions, I then pressed the "up" key for three seconds to set the display at 100%.
Following the "User Settings", I then chose battery capacity as 50AH
-- note, the buttons have to be very firmly pressed, and getting out of
"engineering mode" proved to be difficult.
That's it, I did not set "FULL" and "ZERO" voltages, as that is not a reliable indicator of 100% and 0%.
Using the coulometer
I plugged my Powertech 150W inverter (purchased many years ago from
Jaycar, and used on many camping trips) into a cigarette lighter socket,
and plugged in a desktop lamp:
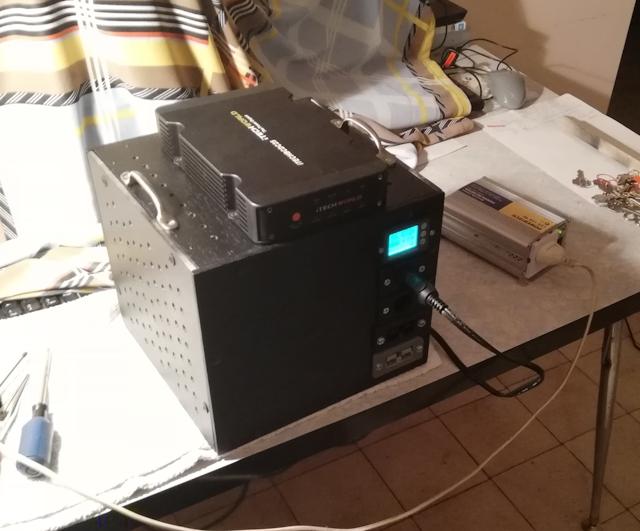

Fantastic, working! Here is the LCD display:

Very nice! That snapshot is after running the lamp for a short time, the capacity has dropped a bit below 50AH.
EDIT 2020-05-04:
After further reflection, I decided it is a good idea to minimize "error
creep" of the State-Of-Charge, by setting a lowest voltage for 0%. See
this later post:
https://bkhome.org/news/202005/coulometer-error-creep.html
Tags: nomad
Wiring-board installed in powerbox
In the previous post, I wrote about some compromises when wiring-up the wiring-board:
https://bkhome.org/news/202004/reflections-on-construction-of-the-wiring-board.html
Now for some photos showing the wiring-board installed. Firstly, here is the wiring-board all ready to be installed:
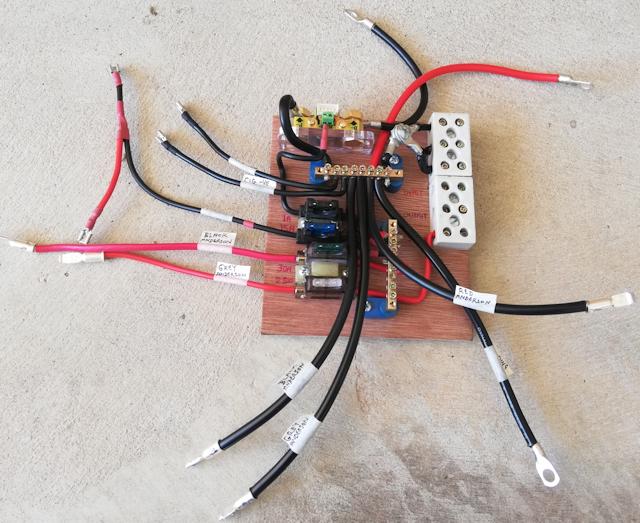
And here it is installed:
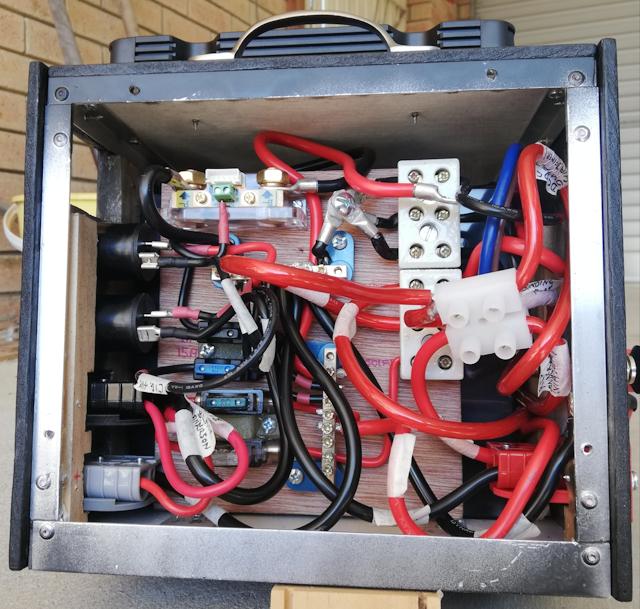
...quite crowded, but more so because of that extra terminal block.
The previous post discussed how that could have been improved, with a
distribution bus mounted on the wiring-board -- there is some space
bottom-right of the board.
I also discussed in the previous post, the limited space to access
the battery terminals. The unconnected eyelet lug in the above photo is
waiting to be bolted to the battery positive terminal. I managed, just,
and solutions to obtain better access are mentioned in the previous
post.
EDIT 2020-05-02:
Both of these problems, battery terminal access and messy floating terminal block, have been fixed. See this later blog post:
https://bkhome.org/news/202004/dc-dc-charger-issues-and-powerbox-improvements.html
Tags: nomad
Reflections on construction of the wiring-board
Continuing the powerbox project, previous post:
https://bkhome.org/news/202004/battery-insertion-and-more-bits-and-pieces.html
The wiring-board has been completed and inserted into the powerbox.
There are a couple of places where I improvised, due to not having the
type of connectors desired...
DC-DC common earth
Top-right of the wiring-board, there are two porcelain terminal
blocks, These will take the wires from the DC-DC charger. The DC-DC
charger has three earth wires (black wires), a "DC input" (red wire), a "DC output"
(blue wire) and "Solar input" (brown wire) wires. The three earth wires
(let's call them "cables" from now on) are electrically connected
together inside the DC-DC charger, so theoretically we only need one of
them. However, for the lowest possible resistance path, I have joined
them via the top terminal block, hence to the "-bus", like this:

...originally, I was going to daisy-chain the left-side terminals,
however, the holes aren't big enough. So, improvised with eyelet lugs
bolted together. What would have been ideal is this (instead of the
porcelain block):
https://www.amazon.com.au/Square-Schneider-Electric-PK4GTACP-Terminal/dp/B00173B1LQ/
...however, that ships from the USA, currently not practical to buy.
This also looks good, though not sure where it ships from (and ideally I
want one that can be affixed to the board, which this doesn't have):
https://www.amazon.com.au/uxcell-Positions-Electric-Distribution-Terminal/dp/B01LWTXOW0/
Incidentally, that 8-way busbar that I have used, two of them, is available in 6-way. Again, I don't know about delivery:
https://www.amazon.com.au/AUTOHAUX-Positions-Terminal-Grounding-DC250V/dp/B07VMD6S3D/
Cable splitter
The second improvisation is splitting a cable. The "DC output" goes
via the porcelain terminal block, to one of the 30A circuit breakers,
hence to the "+bus" busbar. However, I wanted to branch "DC output" to
the +ve binding post -- a convenient place to pickup the +ve voltage
with protection of a circuit breaker.
I cut off two segments of a 60A terminal block, and wired like this:

...you can see "DC-DC output" label, which comes from the "DC output"
of the DC-DC charger. The other side goes to a 30A circuit breaker,
hence to the "+bus". My klutz was to insert two cables into the
left-side of the terminal, bringing out another cable to go to the +ve
binding post.
A 3-way distribution bar mounted on the wiring board would have been far neater.
See bottom-right corner of the photo, "Red Anderson" label. This is
from the other 30A circuit breaker, the other side of which is wired to
"DC input" of the DC-DC charger. As all the cables from the DC-DC
charger and 30A circuit breakers are just bare ends, I need an Anderson lug -- the other terminal
on the terminal block joins a short length of cable with an Anderson
lug on the other end.
This also could have been simplified. The terminal block join could
have been eliminated by soldering an Anderson lug directly onto the
cable from the 30A circuit breaker -- just might need a bigger hole in
the back panel for the cable to feed through to the circuit breaker.
That extra terminal block does look a bit untidy, and clutters things somewhat, but it does the job.
EDIT 2020-05-02:
The messy floating terminal block has been fixed, see this later blog post:
https://bkhome.org/news/202004/dc-dc-charger-issues-and-powerbox-improvements.html
Tags: nomad
Battery insertion and more bits and pieces
The previous post was "bits and pieces" information about construction of the lithium powerbox project:
https://bkhome.org/news/202004/cable-and-soldering-guidelines.html
This post is notes about battery insertion, and various notes about
connectors. In a previous post, I had discussed concerns about the
current capability of some blade fuse holders, and I also mentioned that
spade terminals might not be suitable above 10 amperes -- today's post
has more on this.
Today I inserted the Amptron 50AH lithium battery into the powerbox.
The front and back panels have to be taken off, for insertion of the
bracing bar that will hold the battery down:
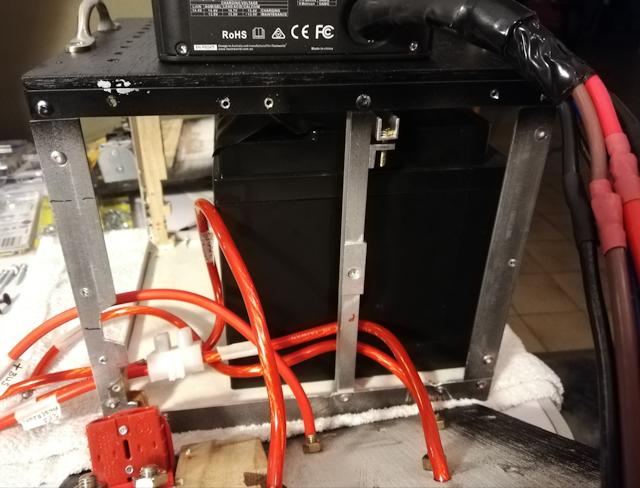

Construction of the bracing bar is described in an earlier post. You
can see it in the above photo, with a bolt that will be adjusted to
provide tension. The bracing bar is 10x10mm aluminium channel, and the
bolt is M4 16mm hex head, purchased from Bunnings:
I used two nuts on each bolt, to lock the nuts.
The battery is held firmly, but just in case, to stop horizontal
creep, I put two pieces of old foam at each end, and on the side of
battery facing the the front panel, put two pieces of 12x20 angle:

WARNING:
As the frame is made with aluminium, I placed electrical tape over the
battery terminals before inserting the battery. Advice to everyone: do
not skip this step!
Also, I wrapped electrical tape around the spanner, for doing-up the terminal bolts. Again, important precaution.
Which reminds me: in a previous post, I suggested that an extra 5mm
height for the box would be an improvement. Yes, I have slim fingers,
but it was difficult to get into the narrow gap between top of battery
and top-inside of the box. Someone with chunky fingers would find it
impossible. Make that an extra 10mm.
Oh, and about the spanner, do not use an adjustable spanner. A proper
flat 13mm (for the Amptron battery) spanner is required. There is just
enough space to slip a spanner over the hex head of the terminals, and
very little swing to tighten it.
At the risk of being overly-verbose in this post, another thought has
occurred to me. I did also mention in an earlier post that a wood frame
might be better than using aluminium. It certainly would be safer when
inserting the battery and accessing the terminals (note, I have not
connected the aluminium frame to either +ve or -ve, which does make it
safer). With a wood frame, the top plate of the box could be screwed
from the top, such that the top plate could be lifted off, thus giving
easy access for both inserting the battery and doing-up the terminals --
worth considering!
I do have thoughts how to design the wood frame, and if anyone wants
to go that way, contact me. Or, if you create a design, let me know and I
can post it.
Now for some connector details...
Washers
The bolts on the battery terminals do not screw all the way down, and
require washers. I have used two washers plus the cable eyelet-lug. The
binding posts also require an extra washer on each. The washer that I
have used for both situations is this:
https://www.bunnings.com.au/pinnacle-m8-stainless-steel-flat-washer-12-pack_p0130534
Also used these in a couple of places, 3/16 inch and M5:
https://www.bunnings.com.au/zenith-3-16-zinc-plated-machine-washer-50-pack_p2420280
Eyelet lugs
Eyelet lugs are required for battery terminals, binding posts,
coulometer shunt, and the 30A circuit breakers. I purchased these two
sizes from Jaycar:
https://www.jaycar.com.au/6mm-non-insulated-eye-terminal-6mm2-pk-8/p/PT4934
https://www.jaycar.com.au/8mm-non-insulated-eye-terminal-10mm2-pk-8/p/PT4936
Spade terminals
I have posted earlier about current capability concerns. As I am
soldering all connections, not crimping, I purchased these female spade
connectors:
https://www.jaycar.com.au/6-3mm-non-insulated-spade-connectors-pk-10/p/PT4630
However, they have very thin metal, and I could feel they had less
grip compared with others that I already have. Those others are going to
be much more suitable for currents up to 15A, but unfortunately are
only available as crimp-type:
https://www.jaycar.com.au/female-spade-yellow-pk-8/p/PT4707
...the plastic covering is very tough, can't even get it off with a
hacksaw, so used my soldering iron to cut down its length. I then had
naked connectors, to which the cable can be soldered. Note, these
connectors will take up to 6mm auto cable.
Rubber feet
The wiring-board is not going to be bolted to the box, instead will
rely on everything around it to keep it in place. There are screws
sticking out the back of it, and as the back side will be against the
battery, I screwed rubber feet onto the back side of the board. These
ones:
https://www.jaycar.com.au/11mm-screw-fixing-rubber-feet-pk-8/p/HP0800
Final product notes
Tomorrow the plan is to do some finishing touches to the assembly,
and powerbox will be ready to go. It is anticipated that the next blog
post will be about the final assembly.
An interesting point about practical usage: the completed powerbox
weighs just on 11kg, which is OK for me, but I wouldn't want to lug
anything heavier. The battery is 50AH, effectively equivalent to an 80AH
AGM battery, which is also OK for me -- but what if one day in the
future, I want to run more things off the battery, or find myself in
situations where there are many days without sunlight, and want more
battery storage?
No problem, just attach another battery. What I would need is another
50AH lithium battery, in a box, with fuse and short cable with a black
Anderson plug. Plug it into the black Anderson plug on my powerbox, and
hey presto, power storage is doubled (make sure both are full-charged
beforehand!). Having two separate boxes is also easier to lift.
My Amptron mains-input lithium battery charger will also have a black
Anderson plug, and can be used to charge either battery.
Tags: nomad
Cable and soldering guidelines
Continuing the lithium powerbox project, this is the previous post:
https://bkhome.org/news/202004/holders-for-blade-fuses-in-powerbox.html
Today's post has some bits and pieces of information about electrical circuit construction techniques. Those who are skilled with soldering, etc., will be OK to construct a powerbox like mine. Others, however, might need some hints.
Cable sizes
I have used various sizes of cable in the powerbox, as you can see in photos posted in earlier blog posts:
https://bkhome.org/news/202004/holders-for-blade-fuses-in-powerbox.html
...the thinner cable is "6mm auto cable", purchased from Big Als via
eBay. This has copper area of 4.59mm2. The thicker cable is two types,
purchased from Altronics. I do have some 8AWG from Big Als, however that
is twin core, besides, I want to use that for extension leads. So I
popped into Altronics and bought one metre of each of their "61A" and
"90A" power cables, red and black. Here are links to the red cable:
https://www.altronics.com.au/p/w4100-630-0.12-red-61a-power-cable/
https://www.altronics.com.au/p/w4216a-119-0.30-90a-red-power-cable/
The differences between these is very interesting. The 61A cable has
thinner strands, which makes the cable more flexible. Here they are
compared with 6mm-auto and AWG sizes:
| Cable type |
Copper area (mm2) |
| 6mm auto |
4.59 |
| 10 AWG |
5.26 |
| 9 AWG |
6.63 |
| W4100 61A |
7.1 |
| 8 AWG |
8.36 |
| W4216A 90A |
8.4 |
Much more expensive buying locally, but ordering over the Internet is
currently very slow, as vendors such as Big Als are based in the
Eastern States. I have used both of those cables from Altronics, using
up what has been purchased.
Soldering
Soldering technique varies, according to individual style. I prefer
the old-school copper tips on soldering irons -- modern irons do have
copper tips, but they are coated with something -- that I file off to
expose the copper -- as I find that solder sticks better to the copper
surface. The copper corrodes, which is why it has the coating,
but I use a file to keep the copper tip clean and flat. I also prefer a
chisel-tip.
This is the iron that I am using for this project:
https://www.bunnings.com.au/tradeflame-60w-240v-soldering-iron-kit_p5910275
...60 watts is more than enough for soldering 8 AWG cable. I use a
wet cloth to wipe the tip of the iron, but it would be nice to have this
one, with stand and sponge:
https://www.bunnings.com.au/tradeflame-30-60w-soldering-iron_p6270385
I do not own a crimping tool, so all joins are soldered. Eyelet lugs
and Anderson plug lugs are connected to cables by the flood-fill method.
See demo here:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6IjG6-PxNBs
...difference for me though, is I apply solder to the expose cable
ends, before inserting. This ensures that solder has flowed through all
the fine wires in the cable, avoiding what is called a "dry join".
The video shows a flame being used to heat the Anderson lug. As I use
a soldering iron, just a dab of solder on the flat surface of the
chisel-tip, held against the side, will heat the wall and the solder can
be inserted -- as the video says, take care not to overfill, otherwise
it will overflow and run down the outside of the lug, perhaps rendering
the lug unusable.
I also solder the ends of the cable that is inserted into screw
terminals. This strengthens the cable, as the twisting action of the
screw can break the fine wires, plus some wires thrust to the side of
the screw are not tightly bonded electrically to the terminal.
Regarding solder, for this fairly heavy work, I prefer 1.6mm thick solder, available from Altronics:
https://www.altronics.com.au/p/t1122-1.6mm-200gm-roll-60-40-leaded-solder/
...Jaycar, only has 1mm solder. Bunnings, on the other hand, only stock much thicker solder, used for plumbing.
Cable splicing
The iTECHBCDC25 DC-DC charger came with Anderson plugs, that I cut
off. It also came with three more Anderson plugs with short lengths of
cable. I need to extend the length of the cables coming out of the DC-DC
charger, so I used the short lengths that were attached to the other
three Anderson plugs. The cable is 10 AWG.
The most common way that two cables are joined together, what we call
"spliced", is a special metal sleeve, which is then crimped. I have
neither the sleeves nor a crimper. Instead, I used this simple method --
just push the two ends into each other.
Doing this, the strands become intertwined, and it will grip
together. Note, I haven't tried this with the ultra-fine copper strands
in the Altronics "61A" cable -- perhaps it might not work. This slightly
out-of-focus photo shows the two cable ends pushed together:

It is then easy to solder, and forms a very strong bond. Heatshrink
tubing needs to be slid over the join. many years ago, I bought a pack
of mixed sizes, and the largest, 6.4mm, fits over 8 AWG cable. Ah yes,
it is still available:
https://www.autobarn.com.au/narva-heatshrink-selection-3-2-6-4-56600
So, there are six Anderson plugs that I have removed the lugs from. I
have plenty other Anderson plugs, but if I wanted to re-use these, it is
possible to buy the lugs, in packs of 20, from eBay.
Tags: nomad
Camping now allowed in WA
In Western Australia we had zero new cases of Covid-19 for three
days, then yesterday there was one, a lady who arrived back from one of
the cruise ships. As long as she hasn't started a new outbreak, things
are looking very good, attributed to the very sensible restrictions
imposed by the WA State government.
Consequently, the Premier today announced some easing of restrictions ...including allowing camping!!!
The eased restrictions are announced here:
Quoting:
non-contact recreational activities such as private picnics in the park, fishing, boating, hiking and camping − all in compliance with travel restrictions and the 10-person rule
WA is broken into regions, and we are still only allowed to drive
within the region in which we live. There are DPAW campsites within the
Perth/Peel Region -- but perhaps lots of people will be taking the
opportunity to go to those campsites.
The main point is though, in theory I can now go camping. Just need
to find a nice bushland or coastal spot within my region, that will not
have many others also camping there.
Got to finish the powerbox first!
Tags: nomad
Holders for blade fuses in powerbox
I posted yesterday about the start of wiring the powerbox, and a problem with using blade fuses at 20-30 amperes:
https://bkhome.org/news/202004/wiring-of-powerbox-underway.html
Originally, I had purchased this blade fuse holder 4-way box:
https://www.autobarn.com.au/narva-fuse-box-blade-54420bl
However, after watching the Redarc video (see above link), I became
concerned. The Narva packaging has "Maximum 30A per circuit", and if you
believe that, then you could put a total of 120A through it, 30A per
fuse.
I did a bit more reading on the topic, and it looks like the 6.3mm
spade terminals, as used in the above Narva fuse box, are only designed
to handle 10-15A. A 6-way blade fuse box sold by Jaycar, which, apart
from having 6 slots looks identical in its internal construction to the
Narva box, states "15A/circuit max" and "45A/block max":
https://www.jaycar.com.au/automotive-fuse-box-6-blades/p/SZ2002
Jaycar have these female spade terminals, rated at 10A maximum:
https://www.jaycar.com.au/6-3mm-non-insulated-spade-connectors-pk-10/p/PT4630
Comparing different blade fuse holders and spade terminals, some are
thicker metal, and appear to be designed to handle higher current.
Looking at what blade fuse holders are on offer, some indeed are
thicker metal and grip the fuse more firmly. I bought two of these
inline blade fuse holders:
https://www.jaycar.com.au/standard-duty-30a-blade-fuse-holder/p/SZ2040
...these have superb grip on the fuse, and actually require some
force to fully insert the fuse. Good, but I want to mount these on my
"wiring-board". That board is 150mm horizontal by 170mm vertical, 6mm
thick marine ply, and I posted a photo of the start of wiring it in the
previous blog post. Here is a photo with two of the inline blade fuse
holders mounted on the board:
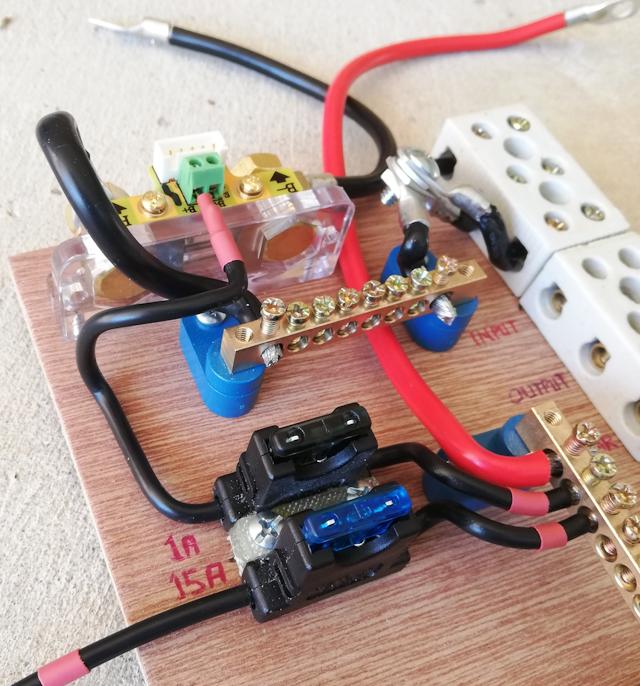
...overkill using that heavy-duty fuse holder for the 1A fuse. To
mount these fuses on the board, I used Selleys "All Plastic Fix" glue
and a small piece of plastic cut off a chopping board.
I have used that Selleys glue on previous projects. It consists of a
primer-stick and an adhesive tube, and will glue all types of plastic,
giving a very strong bond. The primer-stick lasts a lot longer than the
adhesive, and I was reading somewhere, someone just used superglue and
it worked the same as the All Plastic Fix adhesive tube.
The 1A fuse goes to the coulometer, via the shunt. The 15A fuse will
go to the cigarette-lighter sockets. I still have to put in fuse holders
for the DC-output black Anderson plug, and for the solar input grey
Anderson plug -- these will be 30A and 25A fuses.
EDIT 2020-04-26:
Fuse holders for the 30A and 25A blade fuses have been added to the board:
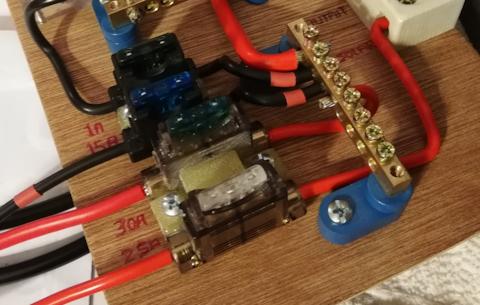
I wanted screw terminals, so chose these:
https://www.jaycar.com.au/screw-terminal-30a-blade-fuse-holder/p/SZ2044
These blade fuses need even more force to
insert than the other ones, so it is a very good connection between fuse
and holder, so I am confident these will handle 30 amperes. The screw
terminal holes look like they will take up to 9 AWG -- I have just
noticed that the table here has the wrong area for 9 AWG cable -- it should be 6.6mm2.
Same construction, the two fuse holders have
been glued together for mounting on the board. Given the force to insert
and remove fuses, I put an extra piece of chopping-board plastic to
more securely bond the two holders together.
The two red cables going out to the left, have
Anderson plug lugs on the ends, for insertion into the black and grey
Anderson plugs.
Tags: nomad
Wiring of powerbox underway
I have started the internal wiring of the lithium powerbox, and
this post is a progress report. Here is the previous post for this
project:
https://bkhome.org/news/202004/powerbox-external-assembled.html
It is progressing slowly, but surely. I had to pause for awhile to
think about some construction details. Anyway, here is a photo showing
the wiring so far:
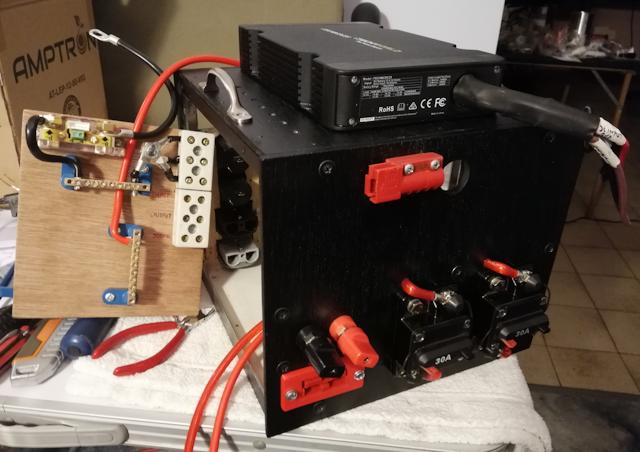

...notice that the box is now painted black! I used a cheap "flat black" enamel paint spray can.
A change from the previous photo (see above link) is that I removed
the Anderson plugs from the DC-DC charger and cut a round hole for the
cables to go into the box. Next to the round hole is "half" of an
Anderson plug -- this is for the wiring to the vehicle ignition key.
The wiring-board is propped alongside the box, for the photo.
Top-left of the wiring-board is the shunt for the coulometer, the two
black and red cables sticking out the top will go to the battery.
The "+bus" and "-bus" busbars were purchased from Jaycar:
https://www.jaycar.com.au/machined-brass-busbar-8-way/p/SZ2003
The terminal blocks at top-right are for wiring to the DC-DC charger. I purchased porcelain blocks:
https://www.jaycar.com.au/3-wire-porcelain-terminal-block-30-amp/p/HM3185
...however, afterward I noticed these, which would probably do the job:
https://www.jaycar.com.au/60-amp-12-way-screw-terminal-strip/p/HM3204
The blank space on the wiring-board is where the fuse holders will
mount. This is where I had some problems, as the blade fuse holders in
local shops, of the surface-mount terminal-block type, seemed too
"light" to handle 20-30 amperes. The engine-bay is a more extreme
environment, but this Redarc video does show the potential for
catastrophic failure when using blade fuses:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=kZ76NsvvBE0
Snapshot from the video, of a melted inline blade fuse holder and fuse:

I intend to post soon about what fuse holders I chose, and what got rejected.
Tags: nomad
